

The human visual system has the capacity to infer the shape of a three-dimensional object using only two-dimensional information.
One of the cues the human visual system uses to perform this inference is shading information.An object's shading is its variation in brightness over a given domain. Computer algorithms have been developed that recover the three-dimensional shape of objects depicted in images. These algorithms are called shape-from-shading algorithms.
Most shape-from-shading algorithms rely on idealistic conditions. They usually assume orthographic projection, a distant point light source, and Lambertian reflectance.
It is known that most real surfaces are neither perfectly diffuse (Lambertian) nor ideally specular (mirror-like); however, most shape-from-shading algorithms assume Lambertian reflectance. It is necessary to develop new techniques to recover the shape of objects whose surfaces are not necessarily Lambertian.
In this research, two algorithms are proposed that can recover the shape of non-Lambertian surfaces given reflectance information. These algorithms are incorporated into the LIRAS (LIght, Reflectance, And Shape) Recovery System. The LIRAS Recovery System is a practical application of computer vision. Given a single image with multiple objects (each having different reflectance properties), the LIRAS Recovery system can reconstruct the three-dimensional shape of each object in the scene. Both real and synthesized images are used to evaluate the proposed algorithms.

Baseball
Original Image Reconstructed Shape using Liras
Plastic Toy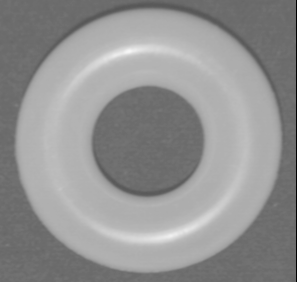
Original Image Reconstructed Shape using Liras
Light Bulb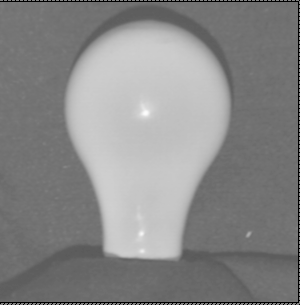
Original Image Reconstructed Shape using Liras

Preliminary results published in:
Bakshi, S. and Y. H. Yang, "Shape From Shading for non-Lambertian Surfaces" IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Austin, Texas Nov 13-16, 1994, Vol II pp. 130-135.
